Understanding Chiplets and Their Impact on Processor Technology
The Basics of Chiplets
Definition and Concept
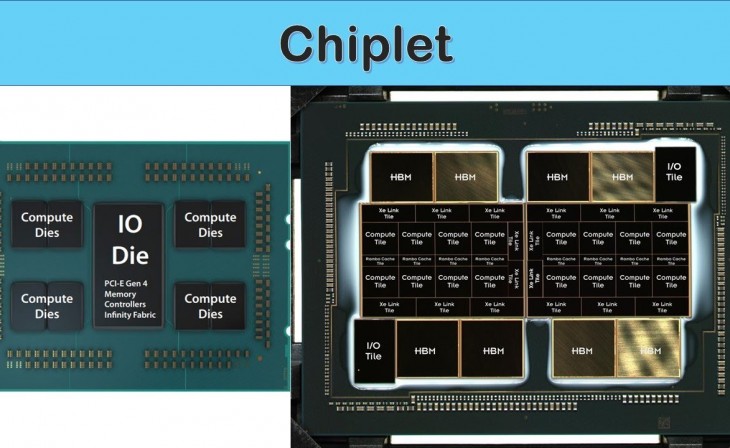
Chiplets are essentially segmented processors. In contrast to the monolithic approach, where all components are consolidated into a single chip, chiplets involve manufacturing specific sections as separate entities. These individual chips are then assembled into one package using a sophisticated connection system.
Advantages of Chiplets
This approach allows for the miniaturization of parts that can benefit from the latest fabrication methods, thereby increasing efficiency and component density. Parts that don't require miniaturization or can't be reduced significantly are produced using older, more cost-effective methods. Overall, this results in a cost-effective and scalable manufacturing process for processors.
The Science Behind Silicon Processors
Manufacturing Process
Processors begin as large silicon wafers, undergoing a series of complex steps to create multiple layers of materials. Patterns are created on these layers through photolithography, with the circular wafer shape leading to some overlap and waste at the edges.
Testing and Binning
Post-manufacturing, wafers undergo electrical testing to assess the quality of each processor. This 'binning' process categorizes each chip based on performance criteria, such as clock speeds and voltage requirements. The wafer is then segmented into individual dies for further assembly and packaging.
Cost and Process Nodes
The cost of manufacturing wafers is significant, with charges varying based on the process node used. The term 'process node' historically referred to the transistor's gate length but has now evolved into a marketing tool. Each new process node offers benefits like reduced cost, lower power consumption, or increased component density.
Also Check Cyberpunk 2077's DLSS and Ray Tracing Performance
The Limitations of Shrinking Processor Components
Challenges with Miniaturization
While logic circuits continue to shrink with advancements in process node technology, analog circuits have seen minimal change, and SRAM is approaching its miniaturization limits. With the increasing proportion of SRAM in CPUs and GPUs, manufacturing all circuitry on the same process node is becoming less cost-effective.
The Divide and Conquer Strategy
Historical Context: Intel's Pentium II
Intel's Pentium II, launched in 1995, was a notable departure from the norm, featuring a main chip and separate SRAM modules for Level 2 cache. This multi-chip approach, sourcing components from different manufacturers, was common in desktop PCs until advancements in semiconductor fabrication allowed for integration into a single die.
The Future of Chiplets in Processor Design
Bridging the Gap
Chiplets offer a solution to the challenges posed by the limits of miniaturization. By dividing a processor into separate components, each can be manufactured using the most appropriate and cost-effective process node. This modular approach not only reduces overall production costs but also allows for greater flexibility and scalability in processor design.
Impact on the Industry
The shift towards chiplets is already making waves in the industry, with leading companies leveraging this technology to enhance performance and efficiency. As chiplets become more prevalent, we can expect a significant transformation in how processors are conceptualized and produced.
Prospects for Innovation
With chiplets, processor companies have a more manageable pathway to expand their product range and innovate. This technology paves the way for more powerful, efficient, and versatile processors, meeting the ever-growing demands of modern computing.
Conclusion: Embracing the Chiplet Revolution
Chiplets represent a crucial evolution in processor technology. By allowing for the separate manufacturing of different processor components, chiplets enable more efficient use of cutting-edge fabrication methods, resulting in more powerful and cost-effective processors. As the industry continues to embrace this technology, chiplets are poised to become the standard in computing, driving innovation and progress in the field.